Nuclear Magnetic Resonance : NMR
Principle
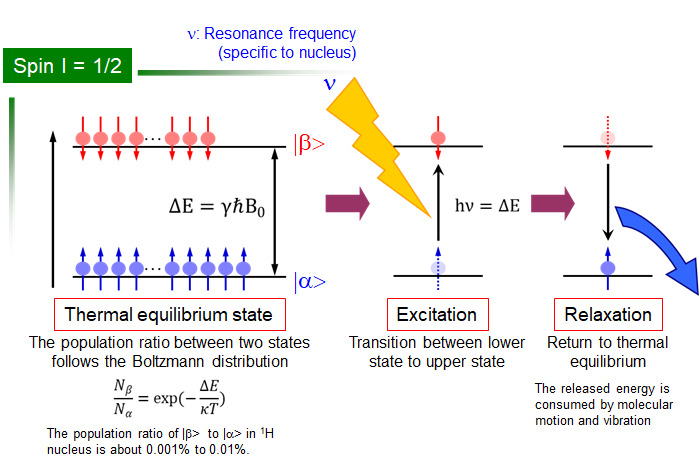
NMR (nuclear magnetic resonance) is a physical phenomenon of nuclear spins placed in the static magnetic field. The nuclear spin (I) placed in the external magnetic field (B0) is degenerate and splits into 2I + 1 energy states. A resonance phenomenon is caused by applying radio wave at the frequency which corresponded to the energy difference between these states. Since a resonance frequency(chemical shift) is related to the degree of electronic shielding around of each nucleus, it is possible to obtain chemical structural information. Moreover, since the process of returning to the thermal equilibrium state after excitation (relaxation process) is deeply related to the fluctuation frequency of the local magnetic field around the nucleus, dynamic information such as molecular motility of a material can be obtained.