- HOME
- Technical Information
- Commissioned Analysis and Research
- X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy : XPS
X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy : XPS
Principle
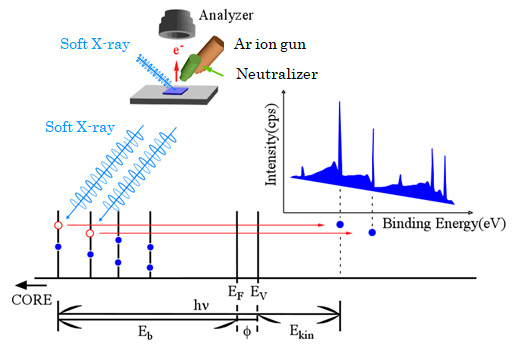
Photoelectron emitted from sample is induced by irradiating soft-X-ray onto sample surface under ultra-high vacuum condition. Elemental composition and chemical states within the surface can be obtained from kinetic energy of photoelectron. Binding energy of photoelectron, Eb, is dominated by photon energy, kinetic energy and work function denoted in the following formula as hν, Ekin and φ, respectively.
Eb = hν – Ekin – φ
As the obtained binding energy of photoelectron is characteristic of the element, the identification of the elements on the surface would be enabled by XPS photoelectron spectrum. Binding states and/or valency reflected in the peak shift (chemical shift) would be, furthermore, valuable information acquired from XPS. A length that photoelectrons can travel through a material (mean free path) is limited to a few nm, which is regarded as information depth of XPS consequently. The XPS analysis could be applied to various materials including insulator. Moreover, depth profiling is also available in combination with ion sputtering with Ar or gas cluster ion beam.