- HOME
- Technical Information
- Commissioned Analysis and Research
- X-ray Absorption Fine Structure : XAFS
X-ray Absorption Fine Structure : XAFS
Principle
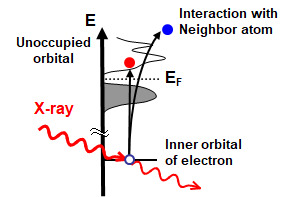
XAFS is x-ray absorption spectrum caused by x-ray irradiation with excitation of inner electron. Information of chemical state and coordination environment of each element can be obtained. XAFS spectrum can be categorized to XANES (X-ray Absorption Near Edge Structure) and EXAFS (Extended X-ray Absorption Fine Structure) along with the difference of x-ray energy region. XANES is the spectrum around the absorption edge and includes the information of chemical state and/or local structure. EXAFS is the oscillation structure in the range from 100 eV to 1000 eV after the absorption edge, therefore it has information of local structure around the designated element.
All sample conditions (solid, liquid and gas) are measureable. Crystallinity, kind of compounds, bonding atoms, orientation as well as chemical state, can be identified. Detection limit could be reached ppm levels in desirable cases. By using in situ techniques, XAFS measurement can be performed under the condition of high temperature and specific gas ambiance.
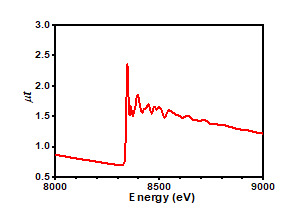
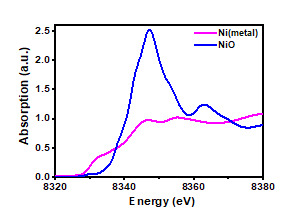
Ni(metal) and NiO