- HOME
- Technical Information
- Commissioned Analysis and Research
- Time of Flight Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometry : TOF-SIMS
Time of Flight Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometry : TOF-SIMS
Principle
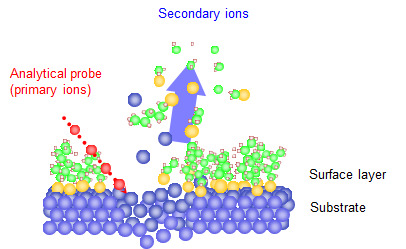
As pulsed primary ion beam is irradiated on a surface of sample introduced in ultra-high vacuum, secondary ions are emitted from the sample surface. Mass spectrum of the components of it would be obtained in consequence of detection of the secondary ions coming through Time-of-flight mass-spectrometer. Limitation of primary ions dose amount provides observation of molecular ions and fragment ions containing the chemical structural information at the surface. Cautious analysis of the mass spectra allows the identification of organic and inorganic matter on the sample surface. By employing focused primary ion beam of less than 1 micrometer, analyses at smaller device or imaging analysis could be conducted for both organic and inorganic materials. Furthermore, TOF-SIMS combined with etching ion beam such as gas cluster ion beam expands the ability to depth profiling and also 3D imaging.
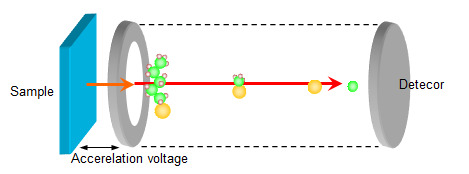
Time-of-flight mass-spectrometer
Each of the secondary ions accelerated with the same energy passes the spectrometer at a speed corresponding to its mass. Because the distance to the detector is constant, the time to reach the detector (time of flight) is expressed as a function of mass. By measuring the distribution of time of flight precisely, the mass distribution of secondary ions (mass spectrum) is obtained.