- HOME
- Technical Information
- Commissioned Analysis and Research
- Dynamic Viscoelastic Method
Dynamic Viscoelastic Method
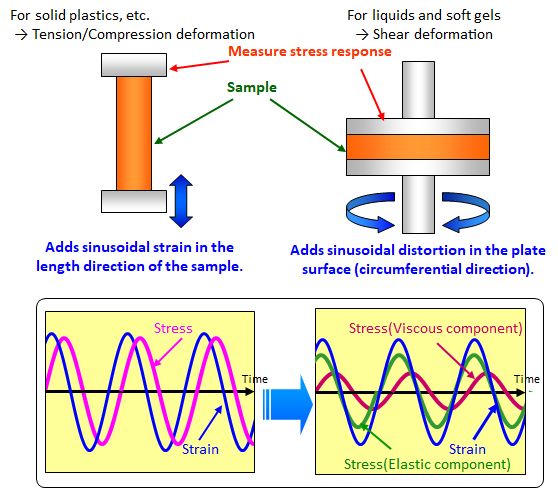
Principle
When a sinusoidal strain of small amplitude is applied to a sample, a sinusoidal stress can be detected in a steady state. The frequency of this stress is the same as that of the strain, but there is a phase delay. The stress can be divided into a component with the same phase as the strain (elastic component) and a component with a 90° phase delay (viscous component). From these components, various viscoelastic parameters (in the case of shear deformation, G': storage modulus, G": loss modulus, G*: complex modulus, η*: complex viscosity, etc.) are calculated.