- HOME
- Technical Information
- Commissioned Analysis and Research
- Raman Spectroscopy:Raman
Raman Spectroscopy : Raman
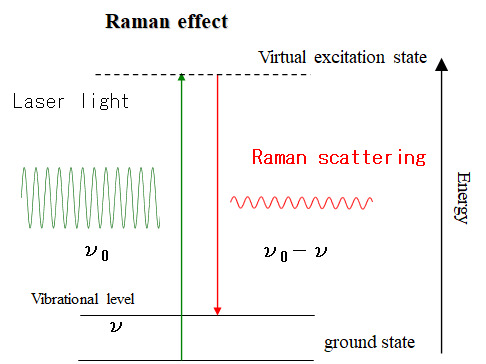
Principle
When a laser beam (monochromatic light) is incident on a molecule or a crystal, it transitions to a vibrational level via a virtual level with a certain probability. At that time, according to the energy conservation law, weak light (Raman scattered light) is generated, which is shifted by the energy of the vibrational mode. The energy shift (Raman shift) of the generated Raman scattered light corresponds to the lattice vibration, and information on the vibration of molecules and atoms can be obtained by spectroscopy.