- HOME
- Technical Information
- Commissioned Analysis and Research
- Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry (ICP-MS)
Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry (ICP-MS)
Principle
Inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) is a type of mass spectrometry that uses an ICP as an ion source. A sample solution is nebulized and introduced into an argon plasma where elements in the sample solution are atomized and ionized. The resulting ions are then brought into the high vacuum region of mass spectrometer via the interface cones. The ions are focused by electrostatic lenses, separated by a mass spectrometer according to their mass-to-charge ratio(m/z), and measured by a detector. There are two types of mass spectrometers: quadrupole and double-focusing.
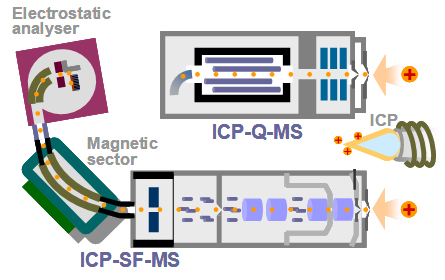
Types of mass spectrometer
● Quadrupole ICP-MS (ICP-Q-MS)
The most commonly used type of mass spectrometer is the quadrupole mass filter. Due to its low mass resolution, there are some instances where this resolution is not sufficient to resolve interferences from polyatomic or isobaric ions.
● Double-focusing magnetic sector field ICP-MS (ICP-SF-MS)
In this type of instrument, both magnetic sector and electric sector are used to separate and focus the ion. This instruments can provide up to 10,000 mass resolution. High mass resolution is used for separation of the spectral interferences.