- HOME
- Technical Information
- Commissioned Analysis and Research
- Infrared Spectroscopy : IR
Infrared Spectroscopy : IR
Principle
When a substance (molecule) is irradiated with infrared light, a certain wavelength range of the infrared light is absorbed by the substance. The wavelength of the absorbed infrared light and the degree of absorption (absorbance or transmittance) vary depending on the substance, making it possible to obtain qualitative analysis of functional groups and information on chemical structures. In addition, according to the Lambert-Beer’s law, absorbance A is proportional to concentration, so it can be applied to quantitative analysis.
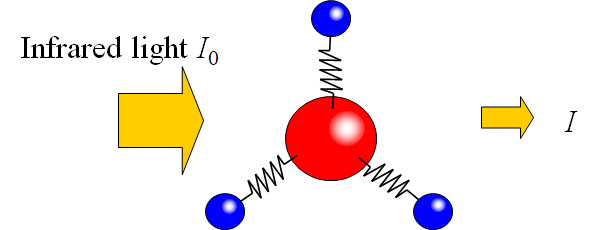
- Transmission spectrum
- T(transmittance) = I /I0
- Absorption spectrum
- A(absorbance) = -log10T
- Lambert-Beer ‘s law
- A = εcl
Thickness: l,concentration: c, molecular extinction coefficient: ε