- HOME
- Technical Information
- Commissioned Analysis and Research
- Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
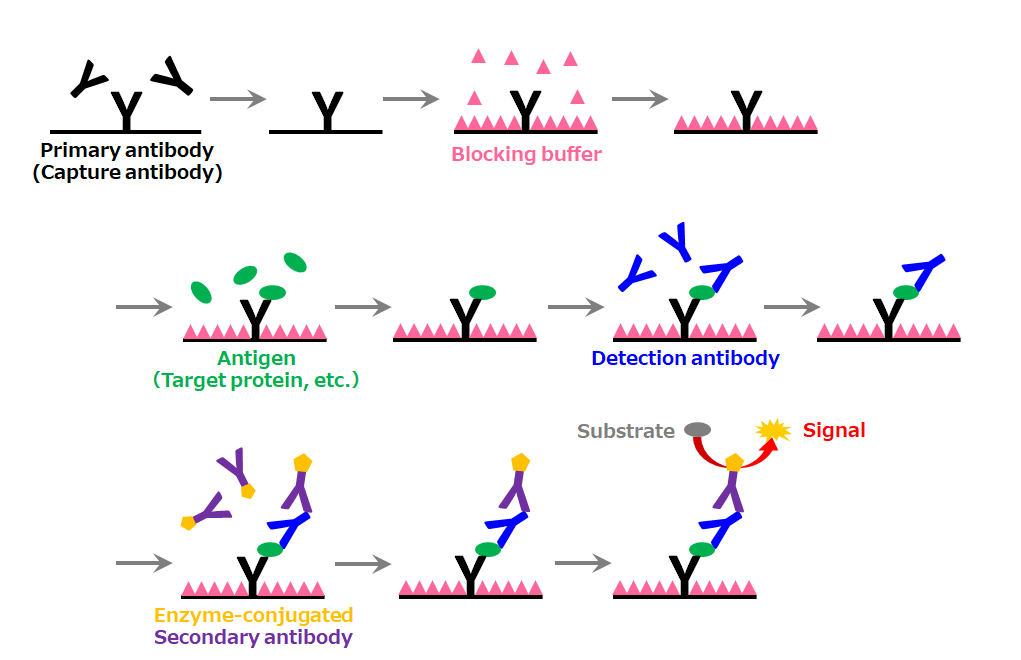
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
Principle
ELISA is a method for measuring the concentration of an antigen (protein, etc.) using antigen-antibody reaction. The antigen-antibody reaction proceeds in the wells of a microplate, which is finally visualized by an enzymatic reaction. By back-calculating from a calibration curve obtained by measuring an antigen of known concentration, the concentration of an antigen of unknown concentration in a sample can be measured. There are several methods such as "Sandwich Method" and "Competition Method", in which the first and second antibodies are used to sandwich an antigen. The principle of the "Sandwich Method" is as follows: