- HOME
- Technical Information
- Commissioned Analysis and Research
- Cathodoluminescence : CL
Cathodoluminescence : CL
Principle
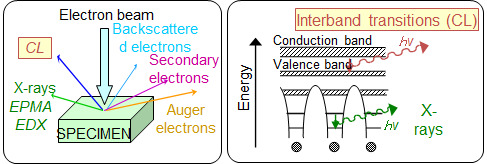
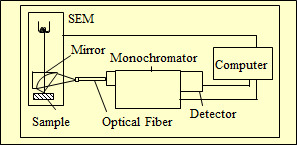
Cathodoluminescence (CL) is a technique that detects the light emitted when a sample is irradiated with an electron beam, allowing analysis of the state of any location while confirming its position in the SEM image. Since CL corresponds to the transition from near the bottom of the conduction band to near the top of the valence band, it reflects the properties of the crystal (crystal defects, impurities, carrier concentration, stress, etc.), not elemental information. Although the information obtained varies depending on the material, it is particularly suitable for evaluating the device state due to its high spatial resolution. A schematic diagram of a typical CL system is shown in Fig. 2. A scanning electron microscope (SEM) is usually used as an excitation source and to confirm the position of the electron beam. The CL from the sample is focused by a focusing mirror and led directly or through an optical fiber to the spectrometer, where it is detected by various detectors.