- HOME
- Technical Information
- Commissioned Analysis and Research
- Capillary Electrophoresis (CE)
Capillary Electrophoresis (CE)
Principle
A sample solution is injected into a fused-silica capillary filled with a buffer solution from an inlet end, and then, by applying a high voltage at both ends of the capillary, ionic species migrate toward an outlet end. The migration rate of each ion is based on its size and mass-to-charge ratio, the separation can be achieved by the difference in mobilities of ions. In the electropherogram, like a chromatogram, of the sample solution obtained by CE, the ionic species is assigned by the migration time of the peak and the concentration is determined by the peak area in comparison with the result of a standard solution. The UV absorbance detector is equipped with the CE instrument. Because of short diameter of the capillary, popularly less than 100µm, the sensitivity is inferior, while the resolution is generally superior to IC.
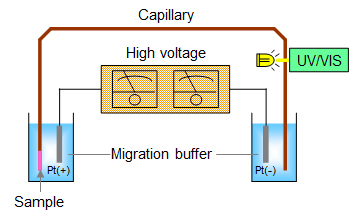
By means of CE, inorganic anions such as chloride and sulfate, organic acids like formate, inorganic cations such as sodium and ammonium ions, amines like tetramethylammonium, in aqueous solutions can be separated. Liquid sample except aqueous solutions and solid samples need to be processed by applying appropriate pretreatment before measurement.