- HOME
- Technical Information
- Commissioned Analysis and Research
- Atomic Absorption Spectrometry (AAS)
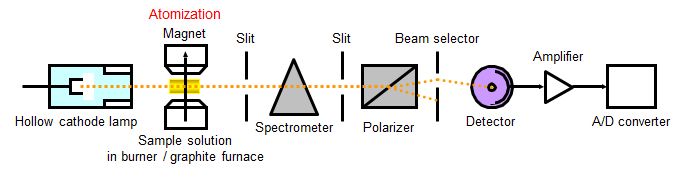
Atomic Absorption Spectrometry (AAS)
Principle
When a sample solution including target elements is heated by flame or graphite furnace, the atomic vapor of the target element is formed. When light with a specific wavelength passes through the vapor, absorption to atoms in incident light takes place. The concentration of the element can be determined from the absorption of this light.
The sample is limited to aqueous solutions for measurement by AAS. Solid samples are need to be processed by appropriate chemical pretreatment.
Atomization
【Flame atomic absorption spectrometry】
A sample solution is atomized and introduced into flame of a mixture of acetylene and air for atomization. This method is suitable for measuring alkali metals such as Na and K with high accuracy.
【Graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry (GF-AAS)】
A sample solution is injected into a graphite furnace, heated to at least 2000°C for atomization. This method is relatively unaffected by coexisting substances and can achieve trace elemental analysis as well as ICP-MS.